Feeling stuck with your GCSE sociology social stratification revision? It is a complex topic, especially if you haven’t used the right resources and techniques. You don’t need to worry, though.
We have gathered the best resources and the key concepts to help you revise. Let’s explore the main topics and questions.
Social Stratification at A Glance
Social stratification is in Paper 2 of the GCSE Sociology exam. To get good grades on your GCSE, revising this sociology section is necessary.
Social stratification refers to dividing people into different layers or classes in society. This division is based on:
- Wealth
- Income
- Education
- Occupation
- Social status.
Classifying people often leads to unequal access to resources and opportunities. On the other hand, social stratification helps organise society by creating clear structures and roles.
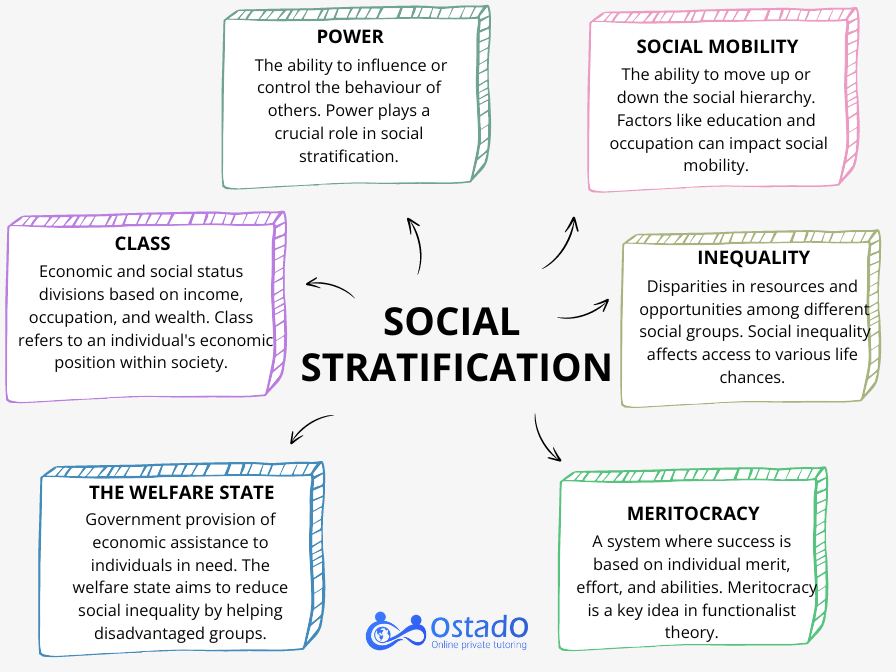
Main Concepts of GCSE Social Stratification
- Class: Divisions based on income, occupation, and wealth.
- Status: Social position or rank.
- Power: The ability to influence or control others.
- Inequality: Disparities in resources and opportunities among different social groups.
- Meritocracy: The key idea in functionalist theory. This system’s success is based on people’s merit, effort, and abilities.
- Relative Poverty: Living standards below the average in society..
- The Welfare State: Government provision of economic assistance to those in need.
What Theories Do You Need to Learn?
These theories form the foundation of many exam questions:
Functionalist Perspective
Functionalists view social stratification as necessary for societal stability and order. They believe that different societal roles require different levels of skill and responsibility.
Stratification ensures that the most qualified people fill the most critical positions. This system motivates individuals to work hard and succeed, which benefits society as a whole. According to functionalists, social stratification creates a meritocratic society with rewards based on achievement and ability.
Key Proponents:
Question example:
- Describe one feature of a meritocracy. (3 marks)
How to approach the question?
Always read the questions carefully. The examiners want you to “describe” something. Give a clear and concise definition or description. Include an example to illustrate your point, if possible.
Conflict Perspective
The conflict perspective sees social stratification as a result of power struggles and inequality. According to this view, society is divided into classes that compete for resources and power.
Marx argued that the capitalist system creates a division between the bourgeoisie (owners) and the proletariat (workers), leading to exploitation and class conflict.
Weber expanded on this by highlighting that stratification involves economic inequality and differences in status and power. Conflict theorists believe that stratification benefits the powerful at the expense of the less powerful, perpetuating inequality.
Key Proponents:
Question example:
- Discuss how far sociologists would agree that the welfare state creates an underclass. (12 marks)
How to answer?
Since this is an essay writing question, you need to structure your answer. Present your arguments with supporting evidence and examples.
Interactionist Perspective
Interactionists focus on the daily interactions and meanings that reinforce social hierarchies. They study how individuals perceive and interpret their social positions and those of others. Goffman’s work on social interaction and identity shows how people use symbols and behaviour to communicate their status.
Interactionists think that everyday actions and interactions keep social stratification in place. These daily practices reinforce accepted social norms and hierarchies. They study how people shape their social identities through these interactions. This helps us understand social inequality better.
Key Proponents:
Question example:
- What term is commonly used by sociologists to describe data that accurately reflects the wider population being studied? (1 mark)
- A) Quota sample
- B) Representative sample
- C) Snowball sample
- D) Systematic sample
How to answer?
For multiple-choice questions, the best strategy is eliminating the wrong choices. Choose the one that you feel more confident about.
How to Get a 9 in GCSE Sociology
GCSE success is mostly about consistency. A realistic GCSE revision timetable will straighten your path. The tips below are proven ways for sociology revision:
-
Expert Help
GCSE sociology is one of the complicated subjects. Many students find expert guidance helpful.
At Ostado we’re here to support you with personalised GCSE tutors tailored to your needs.
We offer free tutorials so that you can only focus on your GCSE success!
-
Mind Maps
are great at organising key concepts and their connections. Visual elements can help you retain information for longer. Plus, they’re fun!
How to make mind maps? Start by writing the main idea at the centre, and add branches of everything you need to learn. Go Conqr offers free mind mapping features for GCSE students.
-
Flashcards
help you memorise definitions, key theorists, and core ideas. Write a term or concept on one side and its explanation on the other.
Quizlet allows you to create your own revision flashcards. Quizlet also has premade flashcards on social stratification for GCSE.

Top Resources and Tools to Ace Your GCSE Sociology
Choosing the right resources can make a big difference in your GCSE Sociology revision. It’s important to pick materials that suit your learning style.
A good tip is to try a few different resources and see which ones help you understand and retain information the best.
The most important factor is consistency, whether you use GCSE revision books or Revision apps.
Textbooks and Study Guides
- AQA GCSE Sociology by Pauline Wilson and Allan Kidd. This textbook covers all key topics and includes practice questions.
- Collins GCSE Sociology by Pauline Wilson. It’s a comprehensive guide with clear explanations and exam tips.
- My Revision Notes: AQA GCSE (9-1) Sociology by Ian Woodfield. This study guide helps with revising key concepts and practising exam techniques.
Useful Websites and Online Courses
- BBC Bitesize Sociology: Offers concise explanations and revision materials tailored for GCSE students.
- Seneca Learning: An interactive platform with quizzes and revision guides for GCSE sociology.
GCSE sociology social stratification revision FAQ
- What is social stratification sociology GCSE?Social stratification in GCSE Sociology is about how society is divided into different layers or classes. These divisions are based on wealth, income, education, occupation, and social status. It organises people into groups, often leading to unequal access to resources and opportunities.
- What did Karl Marx view as social stratification?Karl Marx saw social stratification as a significant issue in capitalist societies. He believed society is split into two main classes: Bourgeoisie: The wealthy owners who control businesses and resources. Proletariat: The working class that sells its labour to the bourgeoisie.
- What Is Covered in GCSE Sociology?GCSE Sociology covers key topics like families, education, crime and deviance, and social stratification. Students learn about different sociological theories and perspectives, as well as research methods used in sociology.

